Copper Clad Laminates: Types, Production Process, and Applications
 08 Apr 2025 14:09:28 GMT
PCBASAIL
08 Apr 2025 14:09:28 GMT
PCBASAIL
What is a Copper Clad Laminate?
A Copper Clad Laminate (CCL), also known as a copper foil base plate, is a composite material. It uses insulating materials (such as glass fiber, polyimide, etc.) as the base material, with one or both sides covered by conductive copper foil. The CCL is the core material for manufacturing Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). It performs functions such as conducting electricity, providing insulation, and offering mechanical support. It is crucial for the performance of PCB products, accounting for 30% of the total cost of a PCB, and direct materials account for approximately 60% of the total cost of a PCB.
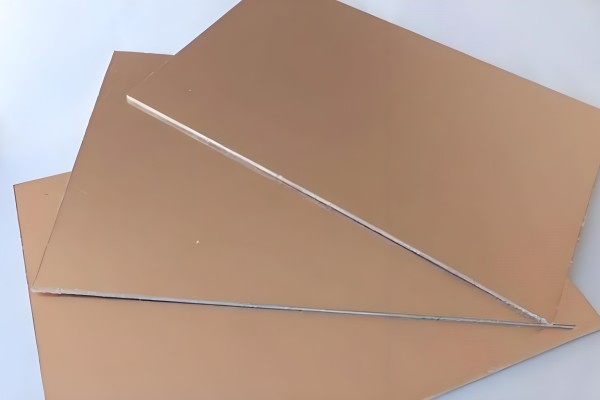

Classification of Copper Clad Laminates
1. According to the mechanical rigidity of the CCL, it can be divided into: Rigid Copper Clad Laminate and Flexible Copper Clad Laminate.
2. According to different insulating materials and structures, it can be divided into: organic resin-based CCLs, metal-based CCLs, and ceramic-based CCLs.
3. According to the thickness of the CCL, it can be divided into: thick boards (with a board thickness range of 0.8–3.2mm (including Cu)) and thin boards (with a board thickness range of less than 0.78mm (excluding Cu)).
4. According to the reinforcing materials of the CCL, it can be divided into: glass cloth-based CCLs, paper-based CCLs, and composite-based CCLs (CME-1, CME-2).
5. According to the flame retardancy grade, it can be divided into: flame-retardant boards and non-flame-retardant boards. According to the regulations of UL standards (such as UL94, UL746E, etc.), the flame retardancy grades of CCLs are classified. Rigid CCLs can be divided into four different flame retardancy grades: namely, UL-94V0 grade; UL-94V1 grade; UL-94V2 grade; and UL-94HB grade.
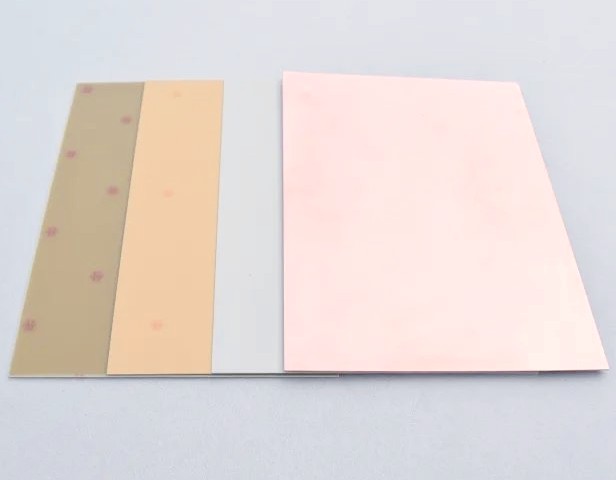
Common Types and Characteristics of Copper Clad Laminates
1. Phenolic Paper-based Copper Clad Laminate: It is a laminated product made by impregnating insulating impregnated paper (TFz-62) or cotton fiber impregnated paper (1TZ-63) with phenolic resin and then hot-pressing. Single sheets of alkali-free glass impregnated cloth can be attached to the adhesive paper on both surfaces, and one side is coated with copper foil. It is mainly used as a printed circuit board in radio equipment.
2. Phenolic Glass Cloth-based Copper Clad Laminate: It is a laminated product made by impregnating alkali-free glass cloth with epoxy phenolic resin and then hot-pressing. One or both sides are coated with copper foil. It has the advantages of being lightweight, having good electrical and mechanical properties, and being easy to process. The surface of the board is light yellow. If dicyandiamide is used as the curing agent, the surface of the board is light green and has good transparency. It is mainly used as a printed circuit board in radio equipment with relatively high operating temperatures and frequencies.
3. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Copper Clad Laminate: It is a type of CCL made by using a PTFE board as the base plate and coating it with copper foil through hot-pressing. It is mainly used as a printed board in high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency circuits.
4. Epoxy Glass Cloth-based Copper Clad Laminate: It is a commonly used material for through-hole metallized printed boards.
5. Flexible Polyester Copper-clad Film: It is a strip-shaped material made by hot-pressing polyester film and copper. In application, it is coiled into a spiral shape and placed inside the equipment. To reinforce it or prevent moisture, it is often poured into a whole with epoxy resin. It is mainly used as a flexible printed circuit and printed cable and can be used as a transition wire for connectors.
Quality Indicators of Copper Clad Laminates
The quality of a CCL directly affects the quality of a printed board. The main non-electrical technical standards for measuring the quality of a CCL are as follows:
1. Copper Cladding Index - Peel Strength: Peel strength is the minimum force required to peel a unit-width copper foil from the base plate, with the unit being kg/cm. This index is used to measure the bonding strength between the copper foil and the base plate. This index mainly depends on the performance of the adhesive and the manufacturing process.
2. Copper Cladding Index - Warpage: Warpage refers to the warpage value per unit length, which is an index for measuring the unevenness of the CCL relative to a plane and depends on the base plate material and thickness.
3. Copper Cladding Index - Flexural Strength: Flexural strength indicates the ability of the CCL to withstand bending, with the unit being kg/cm. This index mainly depends on the base plate material of the CCL. This index should be considered when determining the thickness of a printed board.
4. Copper Cladding Index - Solder Immersion Resistance: Solder immersion resistance refers to the ability of the CCL to withstand the peeling of the copper foil after being placed in molten solder at a certain temperature for a certain period of time (usually 10s). Generally, it is required that the copper foil board does not blister or delaminate. If the solder immersion resistance is poor, the pads and wires of the printed board may fall off during multiple soldering processes. This index has a great impact on the quality of the printed circuit board and mainly depends on the board material and the adhesive.
Production Process of Glass Cloth-based Copper Clad Laminate
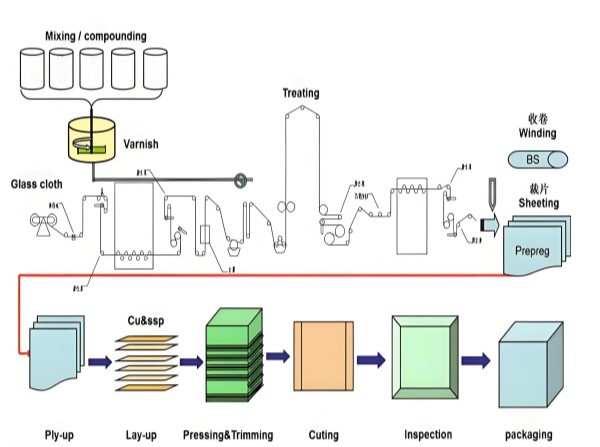
(1) Resin Adhesive Solution Manufacturing
The manufacturing of the resin adhesive solution is completed in a reaction kettle. For the manufacturing of the resin adhesive solution of an epoxy-glass cloth-based CCL, it is mainly the preparation and processing of the resin. That is, the original resin (epoxy resin) provided by a professional resin manufacturer is put into the reaction kettle, and then a curing agent, a curing accelerator, other additives, a solvent, etc. are added and mixed and dissolved to make the solution.
In the resin synthesis reaction and processing, the evaporation area of the reaction kettle (or the diameter-to-height ratio of the reaction kettle) in the equipment design and selection, the pumping rate of the vacuum pump, the condensation area of the condenser, the temperature of the condensed water, the heating and cooling methods of the jacket of the reaction kettle, and the effect of the agitator of the reaction kettle all have an important impact on the performance of the synthesized resin. And the correct and reasonable control of the temperature, vacuum degree, and reaction time in each reaction stage during the manufacturing process is also very important. For the preparation and processing of the resin, it is necessary to strictly control the feeding amount of each component as well as the time and temperature of the mixing and dissolution reactions.
(2) Semi-finished Product Impregnation and Drying Processing
The prepared resin adhesive solution is injected into the glue tank of the gluing machine. Using glass cloth as the reinforcing base material, it is impregnated with the resin adhesive solution, and then it is heated and dried in the oven of the gluing machine at a temperature of 120–180°C to make the resin in a semi-cured state (B-stage resin) and remove the solvent. This process is called gluing, and its product is called glued cloth (also known as a semi-cured sheet, abbreviated as PP, or a prepreg). The processing of the glued cloth for glass cloth-based CCLs is generally carried out in a vertical gluing machine.
The quality control indicators of the glued cloth generally include the resin content (RC%), resin fluidity (RF%), volatile content (VC%), and resin gelation time (GT). Some manufacturers also conduct research and testing on the quality properties of the glued cloth, such as the melt viscosity curve, hydrogen peroxide glue crystallization test, curing percentage, and proportional fluidity.
In the gluing process, the semi-finished glued cloth is completed through two major processing processes of impregnation and drying using the gluing machine. The impregnation process is essentially a process of exchanging the air in the fiber structure of the reinforcing base material with the impregnated resin adhesive solution. During the impregnation process, the resin adhesive solution with appropriate molecular weight, viscosity, and temperature, through the mechanical action of the bottom coating roller (immersing in the resin in one direction) and the extrusion roller (immersing in the resin in both directions and controlling the uniformity of the glue impregnation and the resin content) of the gluing machine, expels the air in the fibers of the reinforcing base material, allowing the resin adhesive solution to occupy its space and form a coating of a certain thickness.
The wet glued cloth after impregnation needs to complete two necessary processes during the drying process in the oven of the gluing machine: one is the evaporation process of the solvent and the low-molecular volatile substances in the resin (including the solvent); the other is the process of the resin molecules continuing to undergo a certain degree of polycondensation. After the drying process is completed, the glued cloth should have only a small amount of volatile components remaining and have a certain degree of soluble resin fluidity suitable for the lamination molding process. The drying process is a process of mutual transformation between the heat transfer of the heat carrier and the mass transfer of the moisture carrier, and it is also a process of transforming the resin structure of the glued cloth from the A stage to the B stage.
(3) Lamination Molding Processing
The entire stage of the lamination molding processing of the CCL mainly includes several main processes such as cutting, stacking, laminating, and unloading the glued cloth.
The stacked blank of the prepared semi-finished glued cloth is covered with copper foil, and copper plates are placed on the top and bottom as molds. Then, it is placed between the heating plates of the press for high-temperature and high-pressure lamination molding processing. The lamination molding processing is completed through three different process control stages: preheating, hot pressing, and cooling. In the lamination processing of glass cloth-based CCLs, in order to improve the performance of the board, the "two-step method" is generally adopted. That is, in the preheating stage, the board is first pressed at a lower temperature and pressure, and then high pressure is applied and the temperature is increased to complete the curing and molding processing of the board.
During the lamination molding processing on the hot press, the resin of the glued cloth first undergoes a short-term melting and re-permeation (this melting and permeation has already occurred in the initial stage of the drying process during the gluing process) in the gaps of the fiber-reinforced base material. Then, through a period of heating reaction, the branched-chain structure of the resin in the B stage transitions to the macromolecular network structure in the C stage, completing the curing and molding to produce a finished product that meets the performance requirements in all aspects.