What is an LED PCB?
A complete guide to LED printed circuit boards
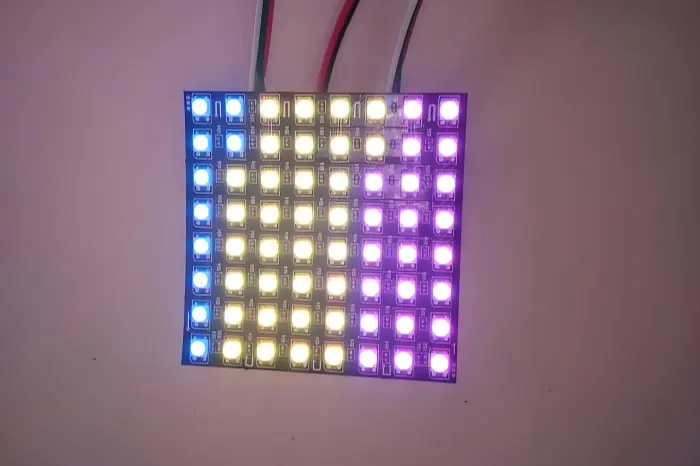

An LED is a Light Emitting Diode. It is a small semiconductor device that turns electricity into light. An LED can make light directly when current flows through it. An LED PCB is a printed circuit board that holds LED packages or LED chips.
The PCB gives the LED a place to sit. The PCB also gives the LED the electric paths it needs. The way the LED is packaged and fixed to the PCB affects how well the LED will work. Key steps in LED packaging are frame mounting, press-welding, and sealing.
LEDs make heat while they work. So LED PCBs often use materials that move heat well. Metal core PCBs and some ceramic PCBs are common. The most common metal core is aluminum. Aluminum is easy to get, moves heat well, has good strength, and gives good cost value.
LED PCB Advantages
High Luminous Efficiency
LED lighting is very efficient. LED lamps can be two to three times more efficient than energy-saving fluorescent lamps. They can be eight to ten times more efficient than old-style incandescent lamps. For the same brightness, LEDs use much less power. This saves energy.
Exceptionally Long Lifespan
The theory life of an LED can reach 100,000 hours. That is far longer than many old light sources. An LED can last roughly 100 times longer than an incandescent lamp. It can last about 20 times longer than a fluorescent lamp. Long life means fewer lamp changes and lower maintenance costs.
Environmentally Friendly
- Free of lead, mercury, and other harmful heavy metals
- Compliant with global standards like RoHS and REACH
- Lower carbon footprint due to energy efficiency
- Reduced waste from longer lifespan
Wide Application Range
- Thin, lightweight design with good mechanical strength and stable structure
- Suitable for outdoor street lights and car headlights
- Ideal for small devices like torches and indicators
- Customizable to meet many needs
LED PCB Materials & Applications
LED PCB Material Comparison
| Material Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Key Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Core | 200–240 | Good heat transfer, cost-effective, lightweight | Street lights, commercial lighting, downlights |
| Copper Core | ~400 | Excellent heat transfer, high durability | Car headlights, stage lights, high-power LEDs |
| Iron Core | ~80 | Low cost, high strength, good stability | Low-power LEDs, stable environment applications |
| FR4 | 0.3–0.5 | Low cost, easy to manufacture | Night lights, decorative lights, indicators |
| Ceramic (AlN) | 140–230 | High insulation, good heat transfer | High-power LED modules, projectors |
| Ceramic (BeO) | ~300 | Excellent heat transfer, high insulation | High-performance LEDs (with safety controls) |
Metal Core Boards
Metal core PCBs move heat well. Heat flows fast in metal. Common metal cores are aluminum, iron, and copper. Aluminum core boards are the current mainstream. They are often used in street lights and commercial lighting.
Copper cores give the best heat move among metal cores. Copper can have a thermal conductivity on the order of 400 W/(m·K), which is much higher than aluminum. This makes copper core boards a good choice for high power scenes, such as car headlights and stage lights.
Iron core boards are cheaper and strong. But iron moves heat less well than aluminum or copper. Iron is used where heat needs are low and stability is more important.
Note: The thermal conductivity numbers in the source text were adjusted for accuracy. For reference, copper's thermal conductivity is near 400 W/(m·K) and aluminum's is near 200–240 W/(m·K).
Fiber (FR4) Boards
FR4 is the common base used in many normal PCBs. FR4 costs less than metal or ceramic. Its heat move ability is low. But FR4 can work for low-power LED uses. Examples are small night lights, decorative lights, and simple indicator lights. For many low-power or low-heat cases, FR4 is good enough and gives low cost.
Ceramic Boards
Some ceramic boards move heat much better than aluminum core boards. Certain ceramic types used for LED modules can have very high thermal conductivity. These boards also give good insulation. Ceramic PCBs suit high-power LED modules and projector light sources.
Types of ceramic used include aluminum nitride and beryllium oxide and alumina. Different ceramics show a wide range of thermal conductivity. Aluminum nitride (AlN) commonly shows values in the range of about 140–230 W/(m·K). Beryllium oxide can show even higher values, up to about 300 W/(m·K) in some forms, though BeO has toxicity limits in some uses. So ceramic choices depend on the exact need and on safety rules.
LED Packaging Forms
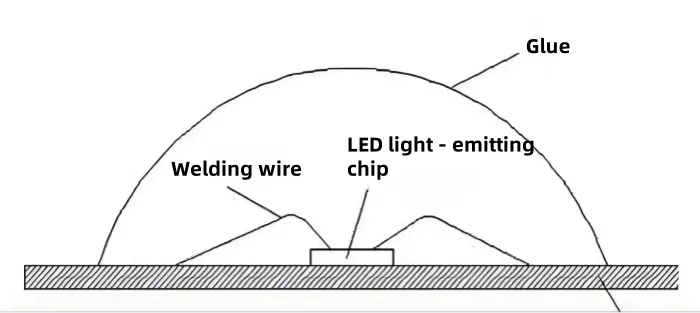
COB (Chip On Board)
COB means Chip On Board. It is a kind of package that is different from DIP and SMD. In LED display and lighting tech, COB means the bare LED chip is fixed on the PCB pad.
- Bare LED chips mounted directly on PCB
- Uses conductive or insulating glue
- Ultrasonic wire bonding for connections
- Epoxy resin sealing for protection
- More compact light surface
- Saves the lead frame or holder component
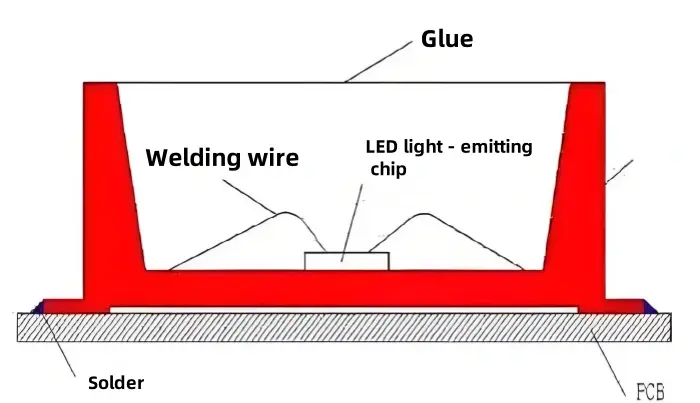
DIP (Dual Inline Pin)
DIP is a simple plug-in package. People also call it plug lamp or insert lamp. DIP was the first of three main package modes to develop. The LED package maker first makes the lamp beads.
- Traditional plug-in package
- Inserted into PCB and wave soldered
- Good for outdoor/robust applications
- Simple design with high durability
- Used in half-outdoor and waterproof modules
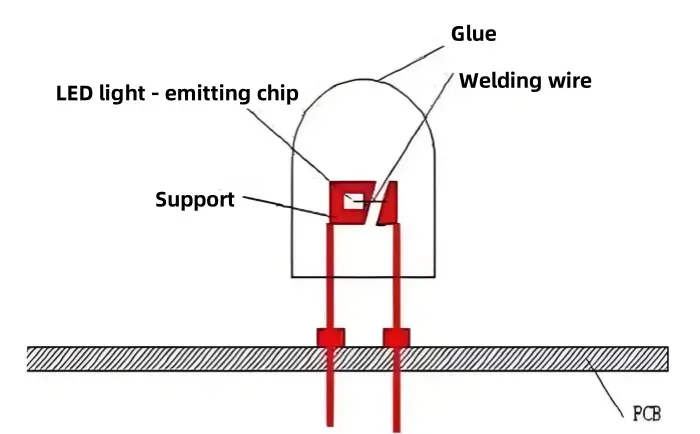
SMD (Surface Mounted Device)
SMD is a form of surface mount tech. It is part of SMT. One common SMD form for LED screens is the "three-in-one" type, where three color LED chips RGB are packaged together.
- Surface mount technology (SMT) compatible
- Common "three-in-one" RGB design
- Uses metal frame/bracket
- Soldered via reflow process
- Compact design for dense displays
- Three color chips in same glue body
LED Packaging Comparison
| Feature | COB | DIP | SMD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Very compact | Larger | Compact |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent | Good | Very good |
| Light Uniformity | Best | Good | Very good |
| Durability | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower | Moderate |
| Soldering Process | Wire bonding | Wave soldering | Reflow soldering |
SMD and DIP packaging use similar die attach and wire bonding steps as COB. The main difference is that SMD and DIP often use a metal frame or bracket. The bracket usually has four solder legs and is soldered to the PCB by SMT or wave soldering.
COB removes this bracket for each single lamp. That saves the step of surface-mount reflow soldering for each lamp bead and can make the final surface flatter.
LED Strip PCBs & Flexible Boards
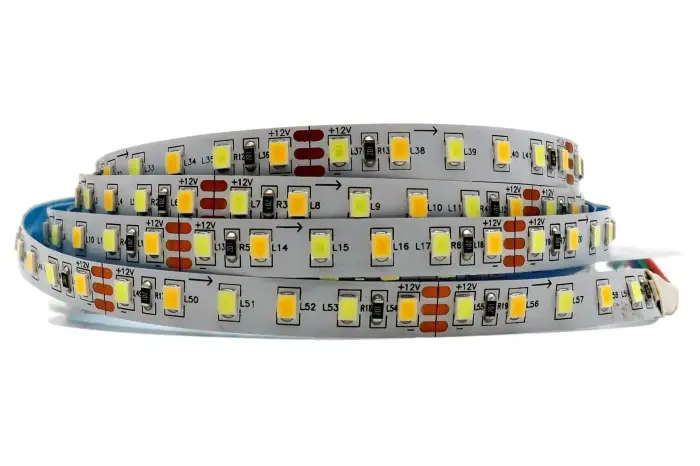

Flexible LED strip PCB
LED strips are flexible LED light bands. They use flexible PCBs. They are soft and bendable. They can fold or roll. They are very flexible and used widely for linear lighting such as decorative strips and signage. Flex PCBs bring new use cases because they can go where a rigid board cannot.
Types of Flexible Circuit Boards
1. Single-sided flex board
Uses a single PI (polyimide) copper-clad sheet. After making the circuit, cover it with one protective film. This gives a single conductor layer soft board.
2. Standard double-sided flex board
Uses a double-sided PI copper-clad sheet. After making circuits on both sides, add protective film on each side. This gives a double conductor soft board.
3. Substrate-generated single-sided board
Uses pure copper foil in making the circuit. Add protective film layers to both sides later. The board ends up with conductor only on one layer but with copper exposed on both sides in some areas.
4. Substrate-generated double-sided board
Uses two single-sided PI copper sheets. A special adhesive with local cutouts can be used between them. Press them together so that in some areas the two layers stay separate. This gives a local double conductor region with high flex in that zone.
These four are the common types of flexible circuit boards.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs
- Can bend, roll, and fold freely. You can place them to fit the available space.
- Using FPC can make devices much smaller in size and weight.
- FPCs can show good heat spread, good solderability, and easy connection.
- The total cost can be low for the final product.
- Access to spaces rigid boards can't reach.

Disadvantages of Flexible PCBs
- High initial cost. Soft PCBs are often custom designs. The cost for design, routing, and photomasks is higher.
- Unless the product needs a soft PCB, the extra cost may not pay off.
- Hard to change or repair. Once made, changes require new artwork or new photomask programs.
- Repairs need removing and restoring the protective film, which is not easy.
- Size limits. Soft PCBs often use step processes, and production gear limits their length and width.
- Easy damage if handled wrong. Poor handling or wrong tooling can hurt them.
- Limited component density compared to rigid PCBs.
- Requires special tooling for manufacturing.
Practical Notes for Designers & Buyers
Key Consideration
Heat management is the most critical factor for LED PCB performance. Poor heat dissipation reduces LED brightness and lifespan significantly.
When LEDs run, the heat must leave the LED area. If heat stays, the LED will lose brightness and life. So choose the right base and thermal path.
Metal core boards give a direct route to move heat away. Copper cores are best for heat move but cost more. Aluminum core boards are a good balance of cost and performance.
Ceramic boards give high thermal conductivity in many cases and also give good insulation and stability. For very high power LED modules, ceramic based PCBs like AlN or BeO may be the right choice. But watch material rules and safety.
For simple, low-power lighting, FR4 is a low-cost choice.
Packaging choice also matters. COB can let more light show and give better uniformity for some lights. SMD is easy to use in compact displays and strips. DIP is still useful for strong outdoor modules.
For strip lights, choose the right flex board type and think of bend radius and mounting. Also check the waterproof needs if the strip will go outdoors or in wet areas.
Final Checklist for LED PCB Orders
- Pick the right base material: aluminum, copper, FR4, or ceramic
- Match the base material to the power level and heat requirements
- Choose appropriate packaging: COB, SMD, or DIP
- For LED strips, select the right flex board type and protective film
- Check RoHS and other regulatory compliance for target markets
- Ask the PCB maker about thermal vias, heat spread layers, and coating options
- Consider waterproofing needs for outdoor or wet environment applications
- Verify copper thickness and core thickness requirements
- Confirm minimum bend radius for flexible LED strips
- Discuss lead time and production volume capabilities
Need an LED PCB Quote?
Get professional pricing for your LED PCB project. Our experts can help select the right materials and packaging for your specific application.
Expert material selection advice
Fast turnaround quotes (within 24 hours)
Thermal management optimization
Common Questions About LED PCBs
Q1: What is an LED PCB?
An LED PCB is a printed circuit board that holds and powers LED chips. It provides electrical connections and helps manage heat produced by the LEDs.
Q2: Why do LED PCBs need metal or ceramic substrates?
LEDs generate heat when working. Metal core PCBs like aluminum or copper, and ceramic boards like AlN, help dissipate heat and extend LED lifespan.
Q3: What are the main advantages of LED PCBs?
LED PCBs offer high efficiency, long lifespan, eco-friendliness, strong structure, and adaptability for many applications such as street lights, headlights, and portable lamps.
Q4: What types of LED packaging exist?
The common packaging forms are COB (Chip On Board), DIP (Dual Inline Package), and SMD (Surface Mounted Device). Each has unique advantages for different applications.
Q5: What are flexible LED PCBs used for?
Flexible LED PCBs, often called LED strips, are used in decorative lighting, signage, and compact electronic products where space-saving and bending ability are required.
Q6: Which substrate is best for high-power LED applications?
For high-power LEDs, copper core PCBs or ceramic PCBs are best. They provide strong heat dissipation and stability in demanding conditions like car headlights or stage lighting.