What is a Flex PCB?
Flex PCB, as the name suggests, is a flexible and bendable printed circuit board (PCB). It is a type of printed circuit board, but differs significantly from traditional rigid printed circuit boards. FPCs typically use PI (polyimide) as their base material, a flexible substance that allows for free bending and flexing. While FPCs are commonly used for connections in components requiring repeated flexing or in small parts, their applications have expanded—most notably, the development of foldable smartphones now relies on FPCs as a key technology.
Composition of Flex PCB Materials
Although the performance of flexible PCB depends on many factors, the main materials play a key role. So, what are the constituent materials of FPC flexible circuit boards? In the structure of FPC flexible circuits, the constituent materials include flexible copper clad laminate (FCCL), coverlay, adhesive film, etc.
Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL)
Common base films of flexible copper clad laminate include polymer plastic films such as polyimide film (PI), polyester (PET), polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), and liquid crystal polymer (LCP). In FPC flexible circuit boards, copper clad laminate mainly undertakes three functions: conductivity, insulation, and support.
Coverlay
It is composed of organic chemical film and adhesive. The function of coverlay is to protect the conductor part of the completed flexible circuit. Adhesive films have different base film and adhesive types, as well as thickness specifications.
Adhesive film
It is formed by coating adhesive on both sides or one side of a base film, and there are also adhesive films with pure adhesive layers without base materials. Adhesive films have different adhesive types and thickness specifications.
Ordinary FPC flexible circuit boards are mainly composed of base material + coverlay. PI is a polyimide insulating resin material, which is characterized by high temperature resistance, good bending performance, and the produced products have good reliability. Its price is more than twice that of PET, and it is the main material of FPC flexible circuit boards.
Need Flexible PCB Solutions?
PCBASAIL provides high-quality flexible circuit boards with adhesive or adhesive-free base materials to meet your specific requirements.
Contact Us for a QuoteAdvantages of Flexible Circuit Boards
Flexible printed circuits are printed circuits made of flexible insulating base materials, with many advantages that rigid printed circuit boards do not have:
- They can be freely bent, coiled, and folded, can be arranged arbitrarily according to the requirements of spatial layout, and can move and stretch freely in three-dimensional space.
- Using FPC can greatly reduce the volume and weight of electronic products, meeting the needs of electronic products for high density, miniaturization, and high reliability.
- FPC has been widely used in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptops, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras and other fields.
- FPC also has advantages such as good heat dissipation, solderability, easy assembly, and relatively low comprehensive cost.
Disadvantages of Flexible Circuit Boards
- High one-time initial cost: Since flexible PCB is designed and manufactured for special applications, the initial costs for circuit design, wiring, and photolithography are relatively high.
- It is difficult to modify and repair flexible PCB: Once a flexible PCB is made, modification must start from the base map or the compiled photoplotter program.
- Size limitation: It is limited by the size of production equipment and cannot be made very long or very wide.
- Easy to be damaged by improper operation: Improper operation by assembly personnel can easily cause damage to flexible circuits.
Common Types of FPC

Single-layer flexible board
It has the lowest cost. When the electrical performance requirements are not high and single-layer wiring is possible, single-layer flexible boards should be used. This most common form has been commercially applied, such as the ink cartridge of printers and the memory of computer systems. A single-layer flexible board has a conductive pattern formed by organic chemical etching, and the conductive pattern layer on the surface of the flexible insulating substrate is rolled copper foil.
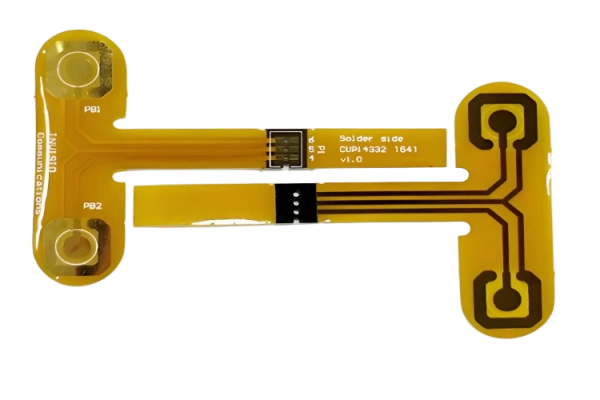
Double-sided flexible board
A double-sided flexible board is a flexible circuit board where conductive patterns are etched on both sides of an insulating base film. Plated through-holes connect the circuits on both sides to form conductive pathways, enabling it to meet the needs of complex circuit designs. Both sides can accommodate circuit routing and component placement. The plated through-hole technology achieves electrical connection between the two sides, while the coverlay protects the circuits and indicates component positions.

Multi-layer flexible board
Multi-layer flexible boards are made by laminating three or more single-layer flexible circuit boards or double-sided flexible circuit boards, forming plated holes through drilling and electroplating, thus forming conductive channels between different layers. In this way, there is no need to use complex welding methods.
It is worth noting that in addition to the number of layers, FPC is also divided into base materials with adhesive and without adhesive. Adhesive-free base materials are better than adhesive-based ones, especially in high-temperature resistance and flexibility. PCBASAIL will provide two options for arbitrary selection, and the default is to use adhesive-free base materials.
Differences Between FPC Components
FPC flexible circuit board is a highly reliable and excellent flexible printed circuit board made of PI polyimide or polyester film as the base material, with the characteristics of high wiring density, light weight, thin thickness, and good bendability. As a special engineering material, PI has been widely used in aerospace, aviation, microelectronics, nanotechnology, liquid crystal, separation membrane, laser and other fields. The long-term service temperature is -200℃~426℃. PI polyimide is very common in FPC flexible circuit boards, existing in base materials, coverlays, and even reinforcements.
| Characteristic | PI Base Material | PI Coverlay | PI Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Base structure of FPC, available with or without adhesive | Insulates the circuit | Increases thickness and hardness of gold fingers for easier plugging |
| Thickness | 1/2mil, 1mil, up to 4-5mil (adhesive-free) | 1/2mil or 1mil | Multiple options: 0.075mm, 0.1mm, 0.125mm, up to 0.25mm |
| Color Options | No color options | Yellow, white, and black | Changes with thickness; darker as it gets thicker |
FPC flexible circuit board can be freely bent, coiled, and folded, can be arranged arbitrarily according to the requirements of spatial layout, and can move and stretch freely in three-dimensional space, thus realizing the integration of component assembly and wire connection. It has been widely used in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptops, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras and other fields.
What are the factors contributing to the processing cost of FPC?
Although the printed circuit board industry shares some common basic processes, the key lies in determining different production processes and equipment based on factors such as substrate thickness and material, precision requirements for line width and spacing, design structure, production scale, and other specific requirements specified by customers.
FPC is a highly customized product, and the factors contributing to the cost of flexible circuit boards are numerous. For new purchasers in electronic manufacturers, it is necessary to understand the factors that make up the cost of FPC flexible circuit boards before conducting flexible circuit board prototyping.
Complexity of Production Processes
The production process of FPC flexible circuit boards is relatively complex, usually involving over 40 processes such as:
In fact, each process of FPC is quite mature, so cost control capabilities have become the most critical factor in the profitability differences among FPC flexible circuit board manufacturers. Cost control is reflected in all aspects of the operation of flexible circuit board manufacturers, directly depending on the company's management level and requiring attention to details.
Cost Composition Breakdown
FPC manufacturers mainly reduce costs by optimizing manufacturing processes and labor efficiency, as copper clad laminate suppliers have strong bargaining power.
Cost reduction strategies include: automation to improve production efficiency, lean management to minimize waste, and technical expertise to reduce rework rates.
PCBASAIL's Cost Control Advantages
- Optimized 40+ production processes through engineering expertise
- Automated production lines improving efficiency and yield rates
- Lean management minimizing material and labor waste
- Transparent pricing with no hidden costs for prototypes or mass production
- Deep supply chain partnerships securing quality materials at reasonable prices
- Balanced customization, precision, and cost efficiency for all order scales
Considering the above factors, smaller quantities may result in higher unit prices due to fixed engineering and setup costs. With PCBASAIL, you get tailored solutions that balance quality and cost efficiency—because great FPCs shouldn’t come with unexpected expenses.
Ready to Get Your Custom FPC Quote?
Based on your material choices, precision requirements, and order scale—we'll provide a transparent quote that reflects the cost factors you've learned.
- No hidden costs for engineering or setup
- Quotes adjusted for your specific process requirements
- Clear breakdown of material, labor, and overhead costs